When it comes to taxes, everyone wants to save money and reduce their liability. That’s where tax planning tips come in to help individuals and businesses navigate the complex world of taxation with ease. From strategies to deductions, this guide has got you covered.
Importance of Tax Planning
Tax planning is essential for individuals and businesses to ensure they are maximizing their financial resources and minimizing tax liabilities. By strategically planning ahead and taking advantage of available tax-saving opportunities, individuals and businesses can significantly reduce the amount of taxes they owe to the government.
Significant Savings
Effective tax planning can lead to significant savings through various strategies such as tax deductions, credits, deferrals, and exemptions. For example, individuals can save money by contributing to retirement accounts like 401(k) or IRA, which not only reduce taxable income but also allow for tax-deferred growth. Businesses can also benefit from tax planning by taking advantage of deductions for expenses like equipment purchases, employee benefits, and research and development.
Consequences of Not Engaging in Tax Planning
Failing to engage in tax planning can result in missed opportunities for tax savings and potential penalties for non-compliance. Individuals and businesses may end up paying more taxes than necessary, leading to financial strain and missed opportunities for investment and growth. Additionally, not being proactive in tax planning can make it challenging to navigate complex tax laws and regulations, increasing the risk of errors and audits.
Tax Planning Strategies for Individuals
When it comes to tax planning, individuals have several strategies they can implement to minimize their tax liabilities and maximize their savings. Let’s take a closer look at some common tax planning strategies that individuals can use to their advantage.
Short-term Tax Planning Strategies vs. Long-term Tax Planning Strategies
Short-term tax planning strategies focus on reducing tax liabilities for the current year, often through deductions or credits that can be immediately applied. On the other hand, long-term tax planning strategies aim to create sustainable tax savings over several years by utilizing investment opportunities, retirement accounts, and other long-term tax-efficient strategies.
Benefits of Tax-efficient Investing for Individuals, Tax planning tips
Tax-efficient investing involves structuring investments in a way that minimizes tax implications, allowing individuals to keep more of their investment returns. By strategically allocating assets in tax-advantaged accounts, utilizing tax-loss harvesting, and considering the tax consequences of investment decisions, individuals can optimize their after-tax returns and build wealth more effectively.
Tax Planning Tips for Small Businesses
When it comes to tax planning for small businesses, there are specific strategies that can help maximize savings and minimize tax liabilities. By taking advantage of tax deductions and credits, small businesses can keep more of their hard-earned money. Additionally, maintaining accurate records is crucial for tax planning purposes, ensuring compliance with tax laws and regulations.
Utilize Small Business Tax Deductions and Credits
- Take advantage of the Section 179 deduction for equipment purchases, allowing you to deduct the full purchase price of qualifying equipment in the year it was purchased.
- Consider the Qualified Business Income deduction, which allows certain small businesses to deduct up to 20% of their qualified business income.
- Explore tax credits available to small businesses, such as the Small Employer Health Insurance Credit or the Research and Development Credit.
Importance of Record-Keeping
Keeping detailed and accurate records is essential for small businesses to support tax deductions and credits claimed on tax returns. It helps in substantiating expenses, income, and other financial transactions, providing documentation in case of an audit. Utilizing accounting software or hiring a professional bookkeeper can streamline record-keeping processes and ensure compliance with tax laws.
Leveraging Tax-Advantaged Accounts: Tax Planning Tips
Tax-advantaged accounts play a crucial role in tax planning by offering various benefits that help individuals and businesses reduce their tax liabilities. By taking advantage of these accounts, taxpayers can optimize their financial strategies and maximize savings.
Types of Tax-Advantaged Accounts
- Retirement Accounts: Contributing to retirement accounts such as 401(k) or IRA can help individuals reduce their taxable income. These contributions are often tax-deductible, allowing taxpayers to save for retirement while lowering their tax bill.
- Health Savings Accounts (HSAs): HSAs are another valuable tool for tax planning, especially for individuals with high-deductible health insurance plans. Contributions to HSAs are tax-deductible, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free. This provides a triple tax benefit, making HSAs a powerful tax-saving vehicle.
- Education Savings Accounts: 529 plans and Coverdell Education Savings Accounts (ESAs) are designed to help families save for education expenses. Contributions to these accounts may be tax-deductible at the state level, and withdrawals for qualified education expenses are tax-free.
Maximizing Tax Deductions and Credits
When it comes to maximizing tax deductions and credits, individuals can take advantage of various opportunities to reduce their tax liability. By understanding the available deductions and credits, as well as implementing effective strategies, taxpayers can optimize their tax savings.
Common Tax Deductions and Credits
- Standard Deduction: A set amount that reduces your taxable income.
- Itemized Deductions: Expenses like mortgage interest, medical expenses, and charitable contributions that can be deducted if they exceed the standard deduction.
- Child Tax Credit: A credit for each qualifying child under the age of 17.
- Earned Income Tax Credit: A credit for low to moderate-income individuals and families.
- Educational Credits: Credits like the American Opportunity Credit and Lifetime Learning Credit for qualified education expenses.
Maximizing Deductions and Credits
- Keep Detailed Records: Maintain thorough records of expenses to ensure you don’t miss any eligible deductions.
- Plan Charitable Contributions: Strategically time donations to maximize deductions, especially when bundling multiple years’ worth of contributions into one tax year.
- Utilize Retirement Accounts: Contributions to retirement accounts like 401(k)s and IRAs can lower taxable income and qualify for credits like the Saver’s Credit.
- Stay Informed: Regularly review tax laws and changes to identify new opportunities for deductions and credits.
Difference Between Tax Deductions and Tax Credits
While deductions reduce taxable income, credits directly reduce the amount of tax owed. Deductions are subtracted from income before calculating tax, whereas credits are applied after tax is calculated, resulting in a dollar-for-dollar reduction in tax liability.
Tax Planning for Investments
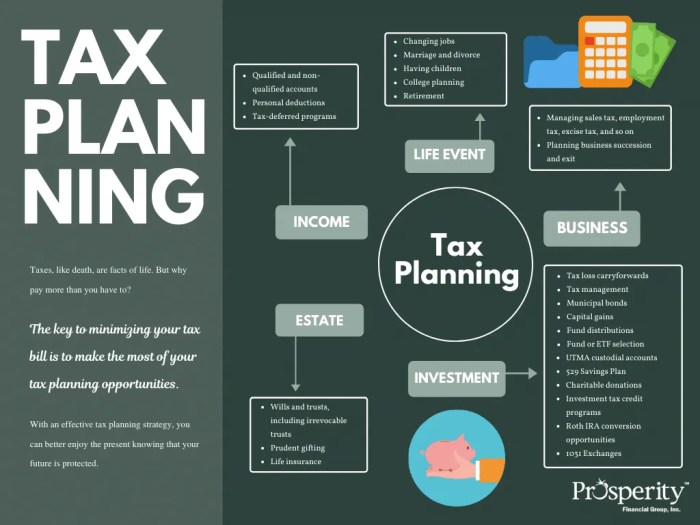
Investing is a key part of building wealth, but it’s important to consider the tax implications of your investment decisions. By utilizing tax-efficient investment strategies, you can minimize the amount of taxes you owe and maximize your returns.
Tax-Efficient Investment Strategies
- Consider investing in tax-advantaged accounts like 401(k)s or IRAs to defer taxes on your contributions and investment gains.
- Focus on long-term investments to take advantage of lower capital gains tax rates for investments held over a year.
- Avoid frequent buying and selling of investments to reduce capital gains taxes and trading fees.
Capital Gains and Losses Impact
- Capital gains are the profits you make from selling an investment, which are taxed at varying rates based on how long you held the investment.
- Capital losses can offset capital gains, reducing your overall tax liability. It’s important to strategically balance gains and losses in your investment portfolio.
Tax-Loss Harvesting
- Tax-loss harvesting involves selling investments at a loss to offset capital gains and reduce your taxable income. This strategy can help lower your tax bill.
- By strategically harvesting tax losses, you can maintain the overall risk and return characteristics of your portfolio while minimizing taxes.
Long-Term Tax Planning Considerations
When it comes to financial decisions, considering the long-term tax implications is crucial. Planning ahead can help minimize tax burdens and maximize wealth accumulation for the future.
Estate Planning Strategies
- Establishing a trust can help protect assets and minimize estate taxes for heirs.
- Regularly review and update beneficiary designations on retirement accounts and insurance policies.
- Utilize the annual gift tax exclusion to transfer wealth tax-efficiently to beneficiaries.
Impact of Tax Law Changes
It’s important to stay informed about changes in tax laws as they can significantly impact long-term tax planning strategies.
- Consult with a tax professional to understand how new laws may affect your financial plan.
- Adjust your tax planning strategies accordingly to take advantage of any new opportunities or avoid potential pitfalls.
