Delving into the realm of Annuities explained, this guide offers a detailed exploration of the intricacies surrounding annuities, shedding light on their significance in financial planning and investment strategies.
As we navigate through the various types, pros and cons, fees, payout options, tax implications, and their role in retirement planning, a comprehensive understanding of annuities will be unraveled.
Annuities Overview
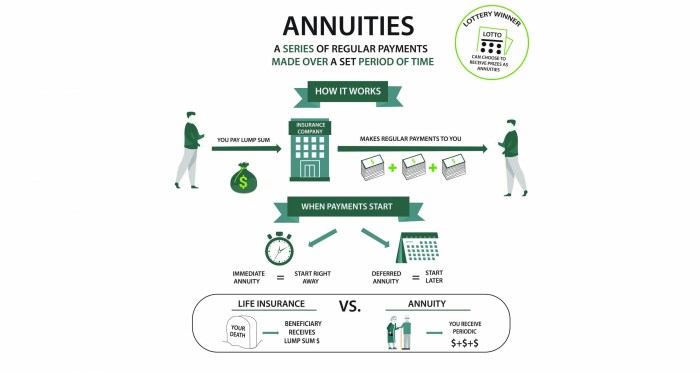
Annuities are financial products designed to provide a steady stream of income over a period of time, often used as part of retirement planning. They are typically purchased from insurance companies and can offer a sense of security for individuals looking for a reliable income source in the future.
Types of Annuities
- Fixed Annuities: These offer a guaranteed payout based on a predetermined interest rate, providing a stable income stream.
- Variable Annuities: The payout fluctuates based on the performance of underlying investments, offering the potential for higher returns but also greater risk.
- Immediate Annuities: Purchased with a lump sum and payments begin immediately, providing an instant income stream.
- Deferred Annuities: Payments begin at a future date, allowing for tax-deferred growth of the funds invested.
Purpose of Annuities in Financial Planning
Annuities play a crucial role in financial planning by offering a way to secure a regular income during retirement years. They can provide peace of mind by ensuring a steady cash flow, helping to cover living expenses and maintain a desired lifestyle. Additionally, annuities can serve as a hedge against outliving one’s savings, offering a reliable source of income for the long term.
How Annuities Work
Annuities function as financial products that provide a steady stream of income over a specified period or for the rest of the annuitant’s life. Individuals typically purchase annuities from insurance companies to secure their financial future.
Annuity Payments and Annuitization
Annuities operate by individuals making premium payments to an insurance company. These payments accumulate over time and earn interest, allowing the annuity to grow. When the annuitant decides to start receiving payments, they can choose between a lump sum payout or periodic payments.
Annuitization is the process of converting the accumulated value of an annuity into a series of payments. This determines the amount and frequency of payments the annuitant will receive.
Role of Insurance Companies
Insurance companies play a crucial role in issuing annuities by managing the funds collected from annuitants and investing them to generate returns. They also assume the risk of providing the guaranteed income stream to the annuitant based on the terms of the annuity contract.
Types of Annuities
When it comes to annuities, there are several types available to investors. Each type has its own features and benefits, catering to different financial goals and risk tolerances.
Fixed, Variable, and Indexed Annuities
- Fixed Annuities: These annuities offer a guaranteed payout over a specified period. The interest rate is usually set at the time of purchase and remains fixed throughout the life of the annuity.
- Variable Annuities: With variable annuities, the returns are tied to the performance of underlying investments, such as mutual funds. This means the payouts can fluctuate based on market performance.
- Indexed Annuities: Indexed annuities offer a return based on a stock market index, such as the S&P 500. They provide the potential for higher returns than fixed annuities while still offering some level of downside protection.
Immediate and Deferred Annuities
- Immediate Annuities: Immediate annuities start paying out income shortly after a lump sum payment is made. They are suitable for individuals looking for a steady stream of income immediately.
- Deferred Annuities: Deferred annuities delay the payment of income until a later date. This allows the invested funds to grow over time before payouts begin and are ideal for individuals planning for retirement in the future.
Features and Benefits
| Type of Annuity | Features | Benefits |
| Fixed Annuities | Guaranteed interest rates | Stable and predictable income |
| Variable Annuities | Potential for higher returns | Opportunity to grow investments based on market performance |
| Indexed Annuities | Participation in stock market gains | Downside protection in volatile markets |
| Immediate Annuities | Immediate income payouts | Steady stream of income for immediate financial needs |
| Deferred Annuities | Tax-deferred growth | Ability to grow investments over time before retirement |
Pros and Cons of Annuities
Investing in annuities can offer a range of benefits and drawbacks that individuals should carefully consider before making financial decisions.
Advantages of Annuities
- Guaranteed Income: Annuities provide a guaranteed stream of income for a specific period or even for life, offering financial security and peace of mind.
- Tax-deferred Growth: Earnings on annuities grow tax-deferred until withdrawals are made, allowing for potential accumulation of wealth over time.
- Flexible Payout Options: Annuities offer various payout options, including lump-sum payments, periodic payments, or a combination of both, allowing customization based on individual needs.
- Protection from Market Volatility: Fixed annuities provide protection from market fluctuations, offering a stable return on investment regardless of economic conditions.
Drawbacks and Risks of Annuities
- High Fees: Annuities can come with high fees, including sales charges, administrative fees, and underlying investment fees, which can eat into returns over time.
- Surrender Charges: Some annuities impose surrender charges if funds are withdrawn before a certain period, restricting access to the invested funds without penalties.
- Lack of Liquidity: Annuities are long-term investments and may lack liquidity, making it difficult to access funds in case of emergencies without facing penalties.
- Inflation Risk: Fixed annuities may not keep pace with inflation, potentially reducing the purchasing power of future income streams.
Comparison with Other Investment Options
- Mutual Funds: Annuities offer guaranteed income, while mutual funds do not provide such assurances. However, mutual funds typically have lower fees and greater liquidity compared to annuities.
- Stocks: Investing in stocks can offer higher potential returns but comes with greater market risk and volatility compared to annuities. Annuities provide a more stable income stream but may offer lower growth potential.
Annuity Fees and Charges
Annuities can be a valuable tool for retirement planning, but it’s important to understand the various fees and charges that come with them. These costs can significantly impact the overall performance of an annuity and eat into your investment returns over time.
Surrender Charges
Surrender charges are fees you may have to pay if you withdraw money from your annuity before a specified time period, typically within the first several years of owning the annuity. These charges can be a percentage of the amount withdrawn and can decrease over time.
Mortality and Expense Fees
Mortality and expense fees are charges deducted from the annuity to cover the insurance company’s costs for providing the death benefit and managing the investment options. These fees are typically a percentage of the account value and can vary depending on the type of annuity.
Administrative Fees
Administrative fees are charged by the insurance company to cover the costs of maintaining the annuity, processing transactions, and providing customer service. These fees are usually a flat dollar amount or a percentage of the account value.
Overall, it’s essential to carefully review the fees and charges associated with an annuity before making a decision to purchase one. Understanding how these costs can impact your investment returns will help you make informed choices and select an annuity that aligns with your financial goals.
Annuity Payout Options
When it comes to annuities, one of the crucial decisions annuity holders need to make is choosing the right payout option. The payout option determines how and when you will receive payments from your annuity. There are different options available, each with its own set of implications and considerations.
Lump-Sum Payment
A lump-sum payment option allows you to receive the full amount of your annuity in one single payment. This can be beneficial if you need a large sum of money for a specific purpose, such as paying off debt or making a big purchase. However, choosing a lump-sum payment means you will no longer receive regular income from your annuity.
Periodic Payments
With periodic payments, you receive regular payments over a set period of time, such as monthly, quarterly, or annually. This option provides a steady income stream and can help with budgeting and financial planning. The amount of each payment is predetermined based on factors like your initial investment, interest rates, and the payout period.
Lifetime Income Stream
Opting for a lifetime income stream means you will receive payments for the rest of your life. This provides a sense of financial security and ensures a steady income in retirement. The amount of each payment is determined by factors like your age, life expectancy, and the terms of the annuity contract. Keep in mind that once you choose this option, payments will continue even if you outlive your life expectancy.
Considerations for Choosing a Payout Option:
– Your financial goals and needs
– Your risk tolerance and investment preferences
– Your current financial situation and retirement plans
– The impact of taxes and inflation on your income stream
Choosing the right payout option is a critical decision that can have long-term implications for your financial well-being. It’s essential to carefully weigh your options and consult with a financial advisor to make an informed choice that aligns with your goals and circumstances.
Tax Implications of Annuities
Annuities come with unique tax implications that investors need to consider when planning their financial future. Understanding how annuities are taxed at different stages, the benefits of tax-deferred growth, and the impact of withdrawals and annuitization on tax treatment is crucial for making informed decisions.
Taxation at Different Stages
Annuities are typically funded with after-tax dollars, meaning the initial premium contributions are not tax-deductible. However, the growth of the annuity is tax-deferred, allowing your investment to grow without immediate taxation on earnings. When you start receiving payments from the annuity, whether through withdrawals or annuitization, the amount you receive will be subject to income tax based on the portion of earnings included in the payment.
Tax-Deferred Growth Benefit
The tax-deferred growth benefit of annuities allows your investment to grow faster compared to taxable accounts since you are not paying taxes on the earnings each year. This compounding effect can lead to significant growth over time, maximizing the potential of your investment.
Impact of Withdrawals and Annuitization
When you make withdrawals from your annuity, the earnings portion of the withdrawal is taxed as ordinary income, while the return of your original investment is not subject to taxation. On the other hand, annuitization involves converting your annuity into a stream of income payments, which are partially taxable based on the exclusion ratio calculated at the time of annuitization.
Annuities in Retirement Planning
When it comes to retirement planning, annuities can play a crucial role in providing a steady income stream during your golden years. By understanding how annuities work and their benefits, you can effectively incorporate them into your overall retirement strategy.
Guaranteed Income Stream
Annuities are unique in that they offer a guaranteed income stream for life or a specified period, providing a sense of financial security during retirement. This can help cover essential expenses and ensure you have a reliable source of income regardless of market fluctuations.
- Annuities can act as a pension-like vehicle, offering regular payments to supplement other retirement savings.
- They can help bridge any income gap that may exist in your retirement plan, providing a stable source of funds.
- By choosing a fixed annuity, you can lock in a set payment amount each month, offering predictability and stability.
Complementing Other Retirement Savings Vehicles
Annuities can work in conjunction with other retirement savings vehicles like 401(k)s or IRAs to create a well-rounded financial plan for retirement. They can provide additional benefits and diversification to your portfolio.
- By combining annuities with retirement accounts like 401(k)s, you can create a diversified income strategy.
- Annuities can offer tax-deferred growth, complementing the tax advantages of traditional retirement accounts.
- They can serve as a longevity hedge, ensuring you have income for life even if you outlive your other savings.
Annuities vs. Life Insurance
When considering financial planning, it is important to understand the differences between annuities and life insurance policies. While both can offer financial security, they serve different purposes and cater to different needs. Let’s delve into the distinctions between annuities and life insurance to help you make informed decisions about your financial future.
Differentiating between Annuities and Life Insurance
Annuities are financial products designed to provide a steady income stream during retirement, typically purchased with a lump sum or series of payments. On the other hand, life insurance policies are intended to provide a death benefit to beneficiaries upon the policyholder’s passing. While annuities focus on income generation, life insurance concentrates on providing financial protection for loved ones in the event of the policyholder’s death.
Financial Needs Addressed by Annuities and Life Insurance
- Annuities are suitable for individuals looking to secure a reliable income stream during retirement, offering a way to manage longevity risk and ensure financial stability in later years.
- Life insurance, on the other hand, is ideal for individuals who want to protect their loved ones financially, providing a death benefit that can cover expenses, debts, or provide an inheritance.
Choosing Between Annuities and Life Insurance
- When deciding between annuities and life insurance, consider your financial goals and priorities. If your primary concern is ensuring a steady income stream in retirement, an annuity may be the better choice. Conversely, if you are more focused on providing financial security for your family in the event of your death, a life insurance policy would be more appropriate.
- It is also possible to have both annuities and life insurance as part of your overall financial plan, depending on your individual circumstances and objectives. Consulting with a financial advisor can help you determine the optimal combination of these products to meet your specific needs.
