As Budgeting techniques takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
Budgeting techniques are essential tools for effective financial management, providing individuals and businesses with a roadmap for success. This comprehensive guide will delve into various budgeting techniques, from traditional methods to modern approaches, offering valuable insights for optimizing financial planning strategies.
Overview of Budgeting Techniques
Budgeting techniques refer to the various methods and strategies used to create, monitor, and manage a budget effectively. These techniques help individuals and businesses allocate resources, track expenses, and plan for future financial goals. By utilizing budgeting techniques, individuals and organizations can make informed financial decisions and ensure financial stability.
Common Budgeting Techniques
- The Zero-Based Budgeting Method: This technique requires assigning every dollar of income a specific purpose, ensuring that all funds are accounted for and allocated efficiently.
- The 50/30/20 Rule: With this method, 50% of income is allocated to needs, 30% to wants, and 20% to savings and debt repayment, providing a balanced approach to budgeting.
- Envelope System: In this technique, cash is divided into envelopes designated for different spending categories, helping individuals limit their expenses and stay within budget.
- Incremental Budgeting: This approach involves adjusting the budget based on past performance and making incremental changes to improve financial planning and decision-making.
Importance of Budgeting Techniques for Financial Planning
Budgeting techniques play a crucial role in financial planning by providing a structured framework for managing income, expenses, and savings. These techniques help individuals and organizations prioritize spending, identify areas of improvement, and work towards long-term financial goals. By implementing effective budgeting techniques, individuals can achieve financial stability, reduce debt, and build wealth over time.
Traditional Budgeting
Traditional budgeting is a method of creating a budget by using previous year’s budget or financial data as a base and making adjustments for the upcoming period. It typically involves incremental changes to the budget based on historical performance and expectations for the future.
Comparison with Modern Approaches
- Traditional budgeting relies heavily on historical data and past performance to set future budgets, while modern approaches like zero-based budgeting start from scratch each budget cycle.
- Modern approaches often involve more frequent reviews and adjustments to the budget, allowing for greater flexibility and responsiveness to changing circumstances compared to the rigid nature of traditional budgeting.
- Traditional budgeting may lead to budget inertia, where organizations continue to allocate resources based on historical patterns rather than current needs or strategic priorities.
Pros and Cons of Traditional Budgeting Techniques
Traditional budgeting techniques have their own set of advantages and disadvantages:
- Pros:
- Provides a sense of stability and predictability in financial planning.
- Easy to implement and understand, especially for organizations with limited resources or expertise in budgeting.
- Helps in setting performance targets based on historical trends and achievements.
- Cons:
- May not account for changing market conditions or unexpected events, leading to potential inefficiencies in resource allocation.
- Less flexible and adaptive compared to modern budgeting approaches, making it challenging to respond quickly to new opportunities or threats.
- Can perpetuate the status quo and hinder innovation by prioritizing past practices over new ideas or strategies.
Zero-Based Budgeting
Zero-based budgeting is a budgeting technique where expenses must be justified for each new budget period, starting from a zero base. Unlike traditional budgeting where the previous period’s budget is the starting point, zero-based budgeting requires every expense to be evaluated and approved, regardless of past budgets.
How Zero-Based Budgeting Works
Zero-based budgeting works by analyzing each expense category from scratch, identifying the needs and costs associated with each one. This method forces individuals or businesses to justify every expense, leading to a more efficient allocation of resources. For example, instead of automatically allocating a certain amount for marketing expenses based on the previous year’s budget, zero-based budgeting would require a detailed breakdown of the marketing needs and costs for the upcoming period.
- Each expense is evaluated independently, without relying on past budgets.
- Focus is on the actual needs and costs of each expense category.
- Encourages efficiency and eliminates unnecessary expenses.
Zero-based budgeting promotes a thorough review of expenses, leading to a more strategic allocation of resources.
Benefits of Zero-Based Budgeting
Zero-based budgeting offers several benefits for individuals or businesses, including:
- Increased cost control and visibility: By scrutinizing each expense, it helps in identifying cost-saving opportunities and eliminating unnecessary spending.
- Resource optimization: It ensures resources are allocated based on current needs and priorities, leading to a more efficient use of funds.
- Enhanced decision-making: With a clear understanding of all expenses, better decisions can be made to achieve financial goals effectively.
Activity-Based Budgeting
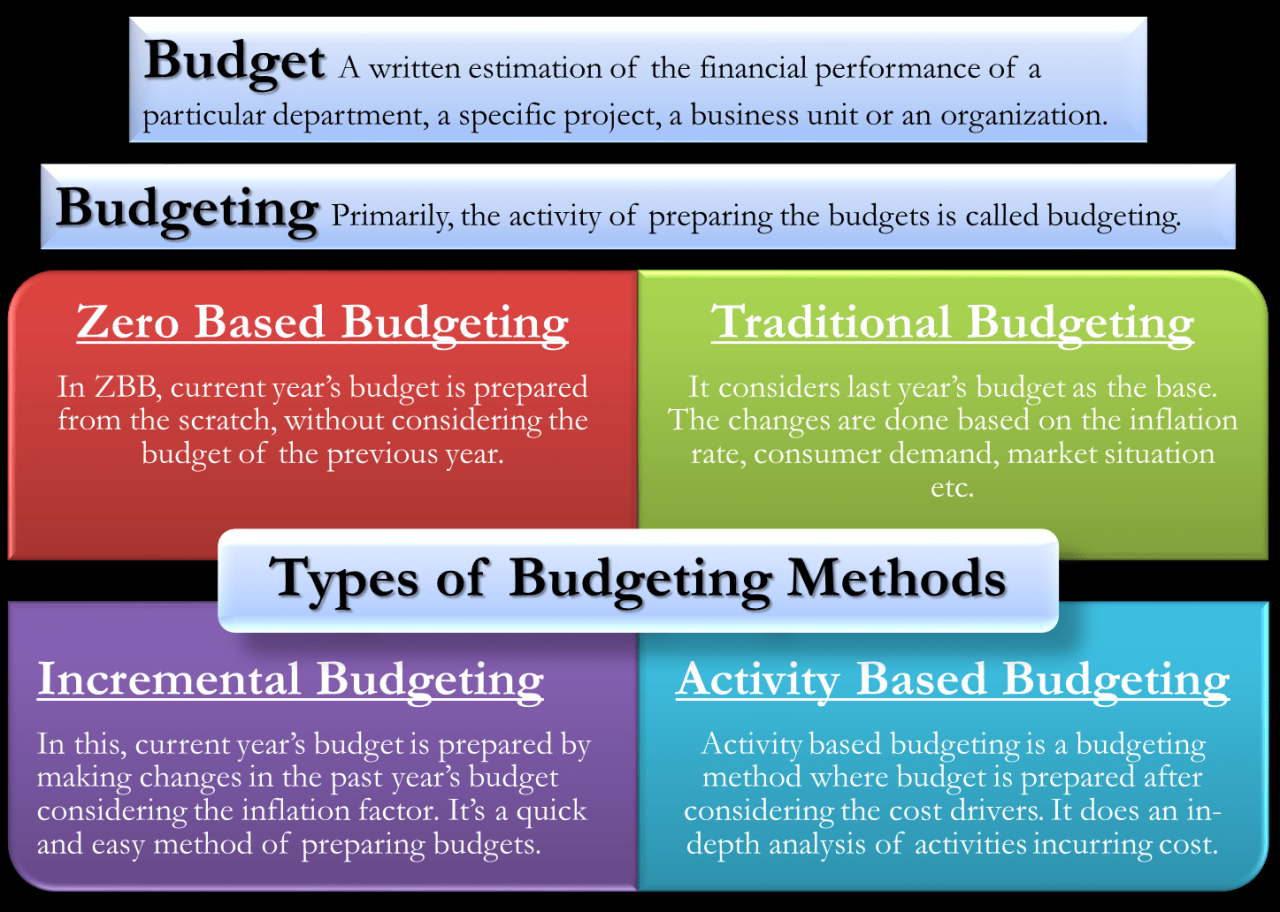
Activity-Based Budgeting (ABB) is a budgeting technique that focuses on linking the budget to specific activities carried out within an organization. This approach allocates resources based on the activities that drive costs, rather than simply relying on historical data or estimates.
Resource Allocation Benefits
Activity-Based Budgeting can help in resource allocation by providing a more accurate and detailed understanding of how resources are utilized within an organization. By identifying and prioritizing activities that directly impact costs, ABB allows for a more efficient allocation of resources to those activities that contribute the most value to the organization.
- By aligning resources with key activities, organizations can optimize their budget allocation and ensure that resources are utilized effectively.
- ABB helps in identifying and eliminating non-value-added activities, leading to cost savings and improved efficiency.
- It enables organizations to allocate resources based on the level of activity, providing a more dynamic and flexible budgeting approach.
Effective Industries and Scenarios
Activity-Based Budgeting is most effective in industries or scenarios where there are complex and diverse activities that drive costs. Industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and service-based organizations can benefit greatly from ABB due to the detailed insights it provides into cost drivers and resource utilization.
- In manufacturing, ABB can help in identifying the cost of different production processes and optimizing resource allocation for maximum efficiency.
- In healthcare, ABB can assist in understanding the costs associated with patient care activities and improving resource allocation to enhance patient outcomes.
- In service-based organizations, ABB can provide a clearer picture of the activities that generate revenue and help in allocating resources to support those revenue-generating activities.
Incremental Budgeting
Incremental budgeting is a financial planning approach where the budget for the upcoming period is based on the current period’s actual results. In this method, the budget is adjusted by a certain percentage or amount from the previous period, taking into account any expected changes or new initiatives.
Advantages of Incremental Budgeting
- Simple and easy to implement, as it builds on existing budgets and historical data.
- Provides stability and predictability, allowing for smoother financial planning.
- Encourages incremental improvements and gradual adjustments over time.
Disadvantages of Incremental Budgeting
- May lead to inefficiencies and waste, as it does not always encourage cost-cutting or optimization.
- Could result in budgetary slack, where departments inflate their budget requests to ensure they are not cut in the next period.
- May hinder innovation and creativity, as it focuses on maintaining the status quo rather than exploring new opportunities.
Real-Life Examples of Incremental Budgeting
One common example of incremental budgeting in action is in government budgeting, where agencies often request budget increases based on a percentage of their current budget. Another example is in corporate budgeting, where departments may receive incremental budget adjustments each year based on past performance and projected growth.
Cash Envelope System
The cash envelope system is a budgeting technique where you allocate a specific amount of cash to different spending categories and keep that cash in separate envelopes. This method helps you to limit your spending and stay within your budget by only using the cash available in each envelope for its designated purpose.
Benefits of Cash Envelope System
- Helps in controlling spending: By using cash for purchases, you are more aware of your spending habits and less likely to overspend.
- Encourages conscious spending: The physical act of using cash makes you think twice before making a purchase, leading to more mindful spending decisions.
- Eliminates the need for credit cards: With the cash envelope system, you rely on the money you have rather than borrowing on credit, reducing the risk of debt accumulation.
Tips for Implementing and Managing the Cash Envelope System
- Create specific categories: Divide your expenses into categories such as groceries, entertainment, transportation, etc., and allocate a set amount of cash to each envelope.
- Label and organize envelopes: Clearly label each envelope with the category name and keep them in a safe and easily accessible place.
- Track your spending: Keep a record of all transactions made using the cash envelopes to monitor your expenditure and ensure you stay within budget.
- Adjust as needed: Regularly review your budget and make adjustments to the cash allocation in each envelope based on your spending patterns and financial goals.
- Stay disciplined: Stick to the cash envelope system and resist the temptation to dip into other envelopes once one category runs out of cash.
Priority-Based Budgeting
Priority-Based Budgeting is a financial planning method that focuses on allocating funds based on the importance of each expense in relation to achieving personal or organizational goals. This approach ensures that resources are directed towards the most critical needs or objectives, helping individuals or businesses make informed decisions about where to allocate their money.
Significance of Priority-Based Budgeting
Priority-Based Budgeting plays a crucial role in financial decision-making by ensuring that limited resources are utilized effectively to meet the most important goals. By aligning spending with priorities, individuals or organizations can avoid unnecessary expenses and prioritize investments that contribute the most towards achieving desired outcomes.
- Identify Financial Goals: Begin by clearly defining short-term and long-term financial goals, whether it’s saving for a house, starting a business, or funding retirement.
- Rank Priorities: Evaluate and prioritize expenses based on their alignment with the established financial goals. Assign a rank or level of importance to each expense category.
- Allocate Funds: Allocate funds according to the priority ranking, ensuring that essential expenses are covered first before moving on to discretionary spending.
- Regular Review and Adjustments: Periodically review the budget to assess progress towards goals and make necessary adjustments based on changing priorities or financial circumstances.
Steps for Creating a Priority-Based Budget
Creating a priority-based budget involves the following steps to ensure that resources are allocated efficiently towards achieving financial objectives:
- Establish Financial Goals: Clearly define short-term and long-term financial goals to guide the budgeting process.
- Evaluate Expenses: Review current expenses and prioritize them based on their relevance to the established goals.
- Allocate Funds: Allocate a portion of the income to each expense category based on its priority level, ensuring that essential needs are met first.
- Monitor and Adjust: Regularly monitor spending patterns, track progress towards goals, and make adjustments to the budget as needed to stay on track.
