Delve into the intricate world of Capital gains tax rates, where financial decisions are intertwined with tax implications. As investors navigate the realm of capital gains, the rates at play hold a significant impact on returns and strategies. Let’s unravel the complexities of Capital gains tax rates to equip you with the knowledge needed for informed decisions.
Overview of Capital Gains Tax Rates
Capital gains tax rates refer to the tax imposed on the profit made from the sale of an investment or asset. These rates are different from ordinary income tax rates, which are applied to wages, salaries, and other sources of income.
It is essential for investors to understand capital gains tax rates as they can significantly impact the returns on their investments. Different tax rates can affect the profitability of investment decisions and the overall portfolio performance.
How Capital Gains Tax Rates are Determined
Capital gains tax rates are determined based on the holding period of the asset and the taxpayer’s income bracket. Short-term capital gains, from assets held for one year or less, are taxed at higher rates compared to long-term capital gains, from assets held for over a year.
The tax rates for long-term capital gains are generally lower to incentivize long-term investments and capital growth. Understanding these rates can help investors strategize their investment decisions to minimize tax liabilities and maximize returns.
Types of Capital Gains Tax Rates
In the realm of capital gains tax, it is essential to understand the different types of tax rates that apply, specifically long-term and short-term rates. These rates play a crucial role in determining the amount of tax owed on any capital gains realized by an individual or entity.
Long-term vs. Short-term Capital Gains Tax Rates
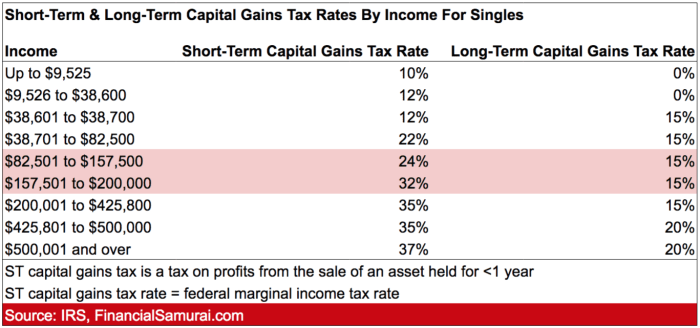
When it comes to capital gains tax rates, the classification of long-term versus short-term is based on how long an asset has been held before being sold. Long-term capital gains are those derived from the sale of assets that have been held for more than one year, while short-term capital gains stem from assets held for one year or less.
- Long-term Capital Gains Tax Rates: Long-term capital gains tax rates are generally lower than short-term rates, as they are designed to incentivize long-term investments. These rates are typically more favorable and can range from 0% to 20%, depending on the individual’s income bracket.
- Short-term Capital Gains Tax Rates: On the other hand, short-term capital gains are taxed at the individual’s ordinary income tax rate, which can be as high as 37%. These rates are higher to discourage short-term trading and promote long-term investment strategies.
It is important to note that the distinction between long-term and short-term capital gains can significantly impact the amount of tax owed on investment returns.
Application of Long-term and Short-term Capital Gains Tax Rates
To illustrate how long-term and short-term capital gains tax rates are applied in practice, consider the following example:
Suppose an individual sells a stock that they have held for over a year and realizes a capital gain of $10,000. If this qualifies as a long-term capital gain and falls within the 15% tax bracket, the individual would owe $1,500 in capital gains tax on this transaction. However, if the same individual sells another stock that they have held for less than a year and realizes the same $10,000 gain, this would be considered a short-term capital gain and taxed at their ordinary income tax rate, potentially resulting in a higher tax liability.
Understanding the distinctions between long-term and short-term capital gains tax rates is crucial for investors to make informed decisions regarding their investment strategies and tax planning. By considering these rates carefully, individuals can optimize their tax liabilities and maximize their investment returns.
Factors Influencing Capital Gains Tax Rates
When it comes to capital gains tax rates, there are several factors that can influence how much tax an individual may owe. These factors can range from changes in tax laws to personal circumstances.
Impact of Tax Laws and Economic Conditions
Changes in tax laws can have a significant impact on capital gains tax rates. For example, if the government decides to increase the tax rate on capital gains, individuals may end up paying more taxes on their investment profits. On the other hand, a decrease in the tax rate can result in lower tax liabilities for investors.
Economic conditions can also play a role in determining capital gains tax rates. During times of economic growth, tax rates may be adjusted to stimulate investment and encourage economic activity. Conversely, in times of economic downturn, tax rates may be increased to generate more revenue for the government.
Personal Circumstances and Capital Gains Tax Rates
Personal circumstances, such as income level, filing status, and holding period, can all affect the capital gains tax rates that an individual may face. Higher income earners are generally subject to higher tax rates on their capital gains, while those in lower income brackets may qualify for lower tax rates or even tax exemptions.
Strategies for Managing Capital Gains Tax Rates
When it comes to managing capital gains tax rates, there are several strategies that can help minimize tax liabilities and optimize your overall financial situation. By employing tax-efficient investment practices and implementing smart tax planning techniques, you can effectively reduce the impact of capital gains taxes on your investment returns.
Utilize Tax-Efficient Investment Practices
One effective strategy for managing capital gains tax rates is to focus on tax-efficient investments. This involves investing in assets that are subject to lower tax rates, such as long-term investments which are taxed at a reduced rate compared to short-term gains. By holding onto investments for longer periods, you can take advantage of favorable tax treatment and potentially lower your overall tax bill.
Implement Tax Planning Techniques
Another key strategy is to implement tax planning techniques to optimize your capital gains tax rates. One common technique is tax-loss harvesting, where you strategically sell investments that have incurred losses to offset capital gains and reduce your taxable income. By carefully managing your investment portfolio and timing your transactions, you can minimize your tax liabilities and maximize your after-tax returns.
Diversify Your Investments
Diversifying your investments across different asset classes can also be an effective strategy for managing capital gains tax rates. By spreading your investments across various sectors and types of assets, you can reduce the impact of capital gains taxes on your overall portfolio. This can help minimize risk and potentially lower your tax burden over time.
