Delving into the realm of budget creation requires a deep understanding of financial management. This guide aims to equip you with essential knowledge and practical tips to navigate the intricacies of budgeting effectively.
Exploring the nuances of financial planning, this guide sheds light on key aspects that can shape your financial future.
Understanding Budgeting
A budget is a financial plan that Artikels an individual’s or organization’s income and expenses over a specific period. It serves as a roadmap for managing finances efficiently and achieving financial goals.
Creating a budget is important for several reasons. It helps individuals track their spending, prioritize expenses, and save for the future. By having a budget in place, one can avoid overspending, identify areas where costs can be reduced, and work towards financial stability.
Benefits of Creating a Budget
- Allows for better financial management
- Helps in setting and achieving financial goals
- Provides a clear overview of income and expenses
- Helps in identifying areas for cost-cutting
- Reduces financial stress and uncertainty
Examples of Financial Goals Achieved through Budgeting
- Building an emergency savings fund
- Planning for a major purchase like a home or vehicle
- Eliminating debt and improving credit score
- Investing for retirement or other long-term goals
Setting Financial Goals
Setting financial goals is a crucial step in creating a budget as it provides direction and purpose to your financial planning. By establishing both short-term and long-term financial goals, individuals can effectively manage their finances and work towards achieving their desired outcomes.
Short-Term and Long-Term Financial Goals
When setting financial goals, it is important to differentiate between short-term and long-term objectives. Short-term goals are typically achievable within a year, such as building an emergency fund, paying off credit card debt, or saving for a vacation. On the other hand, long-term goals are more strategic and may take several years to accomplish, such as buying a home, saving for retirement, or funding a child’s education.
Prioritizing Financial Goals
Prioritizing financial goals involves determining which goals are most important and align with your values and aspirations. It is essential to rank your goals based on their urgency, significance, and feasibility. For example, paying off high-interest debt should take precedence over saving for a luxury purchase.
Examples of Common Financial Goals
- Building an emergency fund to cover unexpected expenses.
- Eliminating credit card debt to improve financial health.
- Saving for a down payment on a house or a car.
- Investing for retirement to secure financial stability in the future.
- Setting aside funds for children’s education to support their future.
Tracking Income and Expenses
Effective tracking of income and expenses is crucial for creating and maintaining a successful budget. By monitoring where your money comes from and where it goes, you can make informed financial decisions and stay on track with your financial goals.
Importance of Categorizing Expenses in a Budget
Categorizing expenses in a budget helps you understand your spending patterns and identify areas where you can cut back or save more. It allows you to see clearly how much you are spending on essentials like housing, groceries, utilities, transportation, and discretionary items like entertainment and dining out. This categorization helps in prioritizing expenses and allocating funds accordingly to meet your financial objectives.
- Fixed Expenses: These are recurring expenses that remain constant each month, such as rent or mortgage, insurance premiums, loan payments, and subscriptions.
- Variable Expenses: These are costs that fluctuate month to month, such as groceries, utilities, transportation, and discretionary spending.
- Savings and Investments: Include contributions to savings accounts, retirement funds, and other investment accounts as a non-negotiable expense in your budget.
- Debt Payments: If you have outstanding debts, like credit card balances or student loans, allocate a portion of your budget to pay them off systematically.
By categorizing your expenses, you can identify areas where you can cut back, reallocate funds, or increase savings, leading to better financial stability and progress towards your financial goals.
Tools or Apps for Tracking Income and Expenses
Utilizing tools and apps can streamline the process of tracking income and expenses, making it more convenient and efficient. Some popular tools include:
| Tool/App | Features |
|---|---|
| Mint | Automatically categorizes transactions, creates budgets, and provides personalized money-saving tips. |
| You Need a Budget (YNAB) | Focuses on zero-based budgeting, tracking every dollar you earn and giving each job to make informed financial decisions. |
| Personal Capital | Offers tools for tracking investments, retirement accounts, and overall net worth in addition to budgeting features. |
These tools can help you gain a comprehensive overview of your financial situation, track your progress, and make adjustments to your budget as needed for better financial management.
Creating a Budget Plan
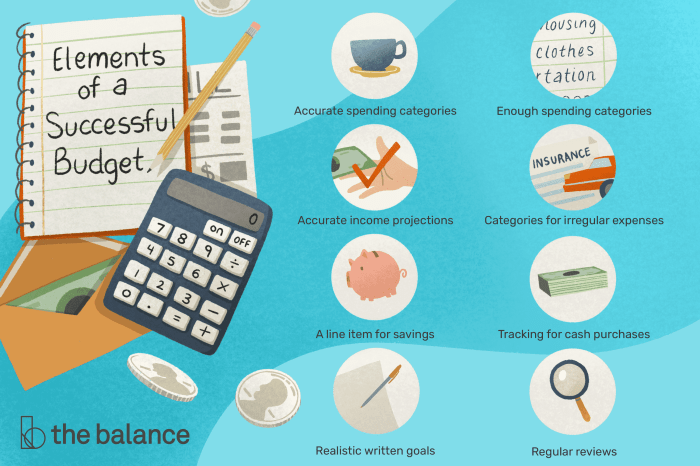
Creating a budget plan is a crucial step in managing your finances effectively. It helps you allocate your income wisely, prioritize your spending, and work towards your financial goals. Here are the steps to create a budget plan from scratch:
Setting Realistic Budget Limits
Setting realistic budget limits is essential to ensure that your budget plan is achievable and sustainable. Here are some tips to help you set realistic budget limits:
- Start by evaluating your current financial situation, including your income, expenses, and any debt you may have.
- Identify your financial goals and prioritize them based on importance.
- Allocate a portion of your income to essential expenses such as rent, utilities, groceries, and transportation.
- Set aside a portion of your income for savings, emergencies, and debt repayment.
- Be realistic about your spending habits and identify areas where you can cut back if needed.
Setting realistic budget limits requires careful consideration of your financial needs and priorities.
Adjusting a Budget Plan
Even with careful planning, you may need to adjust your budget plan from time to time. Here are some tips for adjusting your budget plan as needed:
- Regularly review your budget to track your income and expenses accurately.
- Identify any changes in your financial situation, such as fluctuating income or unexpected expenses.
- Adjust your budget to accommodate any new financial goals or changes in your priorities.
- Consider reallocating funds from one category to another to stay within your budget limits.
- Be flexible and willing to make changes to your budget plan as needed to ensure financial stability.
Saving and Emergency Funds
Having a solid savings plan and emergency fund is crucial in maintaining financial stability and security. Savings help you achieve your financial goals and provide a safety net for unexpected expenses or emergencies.
Building an Emergency Fund
Building an emergency fund within your budget requires discipline and consistency. Here are some strategies to help you establish and grow your emergency fund:
- Set a specific savings goal for your emergency fund. Aim to save at least three to six months’ worth of living expenses.
- Automate your savings by setting up automatic transfers from your checking account to your savings account each month.
- Cut back on non-essential expenses and redirect those funds towards your emergency fund.
- Consider additional sources of income, such as freelance work or selling items you no longer need, to boost your savings.
Recommended Percentage of Income for Savings
Financial experts often recommend allocating 20% of your income towards savings. This includes saving for retirement, building an emergency fund, and achieving other financial goals. By prioritizing savings in your budget, you can secure your financial future and be better prepared for unexpected expenses.
Managing Debt
Effectively managing and paying off debt is crucial in achieving financial stability. By incorporating debt repayment strategies into your budget plan, you can work towards reducing and eliminating your debts over time.
Debt-to-Income Ratio and Its Significance
The debt-to-income ratio is a financial metric used to measure an individual’s debt relative to their income. It is calculated by dividing total monthly debt payments by gross monthly income. This ratio provides insight into an individual’s ability to manage and repay their debts, with lower ratios indicating better financial health.
Having a high debt-to-income ratio can signify financial distress and may make it challenging to keep up with debt payments. By understanding and monitoring this ratio, you can assess your financial situation and make informed decisions to improve it.
Prioritizing Debt Repayment in a Budget Plan
- Identify High-Interest Debts: Start by listing all your debts and identifying those with the highest interest rates. These debts typically cost more over time, so focusing on paying them off first can save you money in the long run.
- Minimum Payments: Ensure you make at least the minimum payments on all your debts to avoid penalties and maintain a good credit score.
- Snowball vs. Avalanche Method: Consider using the debt snowball method, where you pay off the smallest debts first to gain momentum, or the debt avalanche method, where you prioritize debts with the highest interest rates for cost-efficiency.
- Allocate Extra Funds: If you have extra money in your budget, allocate it towards debt repayment. This can accelerate the payoff process and reduce the total interest you pay.
- Stay Consistent: Make debt repayment a priority in your budget plan and stay consistent with your payments. Over time, you will see progress towards becoming debt-free.
