Delving into the intricate world of Interest rates and mortgages, this opening paragraph aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the topic, shedding light on the crucial relationship between interest rates and mortgage payments. We will explore the various types of mortgages, factors influencing interest rates, and the concept of mortgage refinancing. Join us on this journey as we unravel the complexities of this financial landscape.
Importance of Interest Rates
Interest rates play a crucial role in the housing market, particularly when it comes to mortgages. Let’s delve into the relationship between interest rates and mortgages, how they impact mortgage payments, and the overall effect on the housing market.
Impact on Mortgage Payments
Interest rates directly affect the cost of borrowing money for a mortgage. When interest rates are low, borrowers can secure loans at lower rates, resulting in lower monthly mortgage payments. Conversely, when interest rates are high, borrowers end up paying more in interest, leading to higher monthly payments.
Effect on the Housing Market
Changes in interest rates can have a significant impact on the housing market. For example, when interest rates are low, more people are inclined to buy homes due to the affordability of mortgages. This increased demand can drive up housing prices. On the other hand, when interest rates are high, fewer people may be able to afford homes, leading to a decrease in demand and potentially lower housing prices.
Types of Mortgages
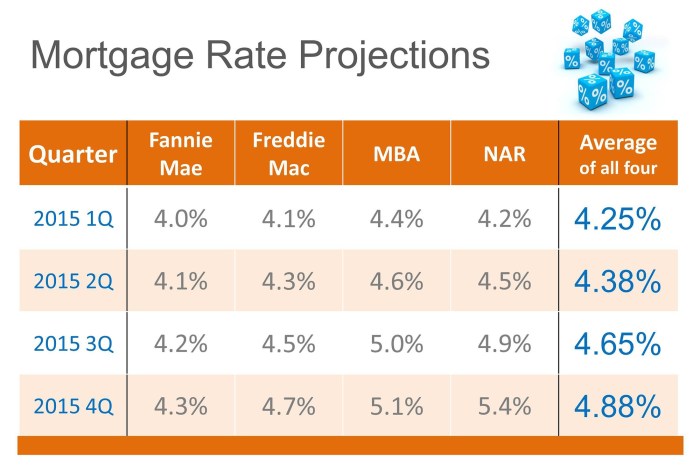
When it comes to mortgages, there are several types of loans available to borrowers. Each type has its own unique features and benefits, so it’s important to understand the differences before making a decision.
Fixed-Rate Mortgages
A fixed-rate mortgage is a loan where the interest rate remains the same throughout the life of the loan. This means that your monthly payments will also remain constant, providing predictability and stability. Fixed-rate mortgages are popular among borrowers who prefer consistency and want to avoid fluctuations in their payments.
Some pros of fixed-rate mortgages include:
• Predictable monthly payments
• Protection against rising interest rates
• Easier budgeting and planning
However, some cons of fixed-rate mortgages are:
• Higher initial interest rates compared to adjustable-rate mortgages
• Less flexibility if interest rates decrease
Adjustable-Rate Mortgages
An adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM) is a loan where the interest rate can change periodically based on market conditions. This means that your monthly payments can fluctuate, potentially increasing or decreasing over time. ARMs typically have lower initial interest rates compared to fixed-rate mortgages.
Some pros of adjustable-rate mortgages include:
• Lower initial interest rates
• Potential for lower payments if interest rates decrease
• Flexibility to take advantage of falling interest rates
However, some cons of adjustable-rate mortgages are:
• Uncertainty in future payments due to interest rate fluctuations
• Risk of higher payments if interest rates rise
It’s essential to carefully consider your financial goals and risk tolerance when choosing between fixed-rate and adjustable-rate mortgages, as each type has its own advantages and drawbacks. Make sure to compare the terms and conditions of different mortgage options to find the best fit for your individual needs.
Factors Influencing Interest Rates
Interest rates for mortgages are influenced by a variety of factors that impact the overall economy. Understanding these factors is crucial for borrowers and investors alike to make informed decisions. Let’s delve into the key determinants of interest rates for mortgages.
Economic Conditions
Economic conditions play a significant role in determining interest rates for mortgages. In times of economic growth and low unemployment rates, interest rates tend to rise as demand for loans increases. Conversely, during economic downturns, interest rates may decrease to stimulate borrowing and spending.
- Low Unemployment: Low unemployment rates are often associated with higher interest rates, as lenders perceive lower risk in lending money.
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): A strong GDP growth can lead to higher interest rates, reflecting a robust economy.
- Consumer Confidence: Positive consumer sentiment can drive interest rates up, signaling optimism about the economy.
Inflation and Federal Reserve
Inflation and the Federal Reserve also play a crucial role in shaping interest rate movements. Inflation refers to the increase in prices of goods and services over time, leading to a decrease in purchasing power. The Federal Reserve, as the central bank of the United States, implements monetary policies to control inflation and stabilize the economy.
When inflation is high, the purchasing power of the dollar decreases, leading lenders to charge higher interest rates to compensate for the eroding value of money.
- Inflation Rate: Higher inflation rates can trigger the Federal Reserve to raise interest rates to curb inflation and maintain price stability.
- Federal Reserve Policies: The Federal Reserve’s decisions on monetary policy, such as adjusting the federal funds rate, can directly impact interest rates for mortgages.
- Market Expectations: Anticipation of future inflation and Federal Reserve actions can also influence current interest rates in the mortgage market.
Mortgage Refinancing
When it comes to mortgage refinancing, it involves replacing your current mortgage with a new one, usually to take advantage of better interest rates, change the loan term, or tap into the equity of your home.
Benefits of Refinancing Based on Interest Rates
- Lower Interest Rates: Refinancing can be beneficial when interest rates drop significantly from when you initially took out your mortgage. This can result in lower monthly payments and long-term savings.
- Switching from Adjustable Rate to Fixed Rate: If you have an adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM) and want more stability, refinancing to a fixed-rate mortgage can protect you from future rate increases.
- Shortening Loan Term: Refinancing to a shorter loan term can help you pay off your mortgage faster and save on interest payments over time.
Process of Refinancing and Considerations
- Evaluate Your Financial Situation: Before refinancing, assess your current financial status, credit score, and home equity to determine if it makes sense.
- Compare Offers: Shop around and compare offers from different lenders to ensure you get the best deal in terms of interest rates, closing costs, and loan terms.
- Calculate Costs and Savings: Consider the closing costs associated with refinancing and calculate how much you can save in the long run to determine if the refinance is worth it.
- Choose the Right Time: Timing is crucial when refinancing. Keep an eye on interest rate trends and make a move when rates are favorable to maximize your savings.
