As Retirement age statistics takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
Retirement age statistics provide valuable insights into the changing landscape of global demographics and workforce trends. Understanding the factors that influence retirement age can shed light on societal norms, economic conditions, and gender disparities. In this comprehensive discussion, we delve into the intricate details of retirement age statistics, examining various trends and factors that shape retirement decisions worldwide.
Overview of Retirement Age Statistics
Retirement age statistics refer to data and information related to the age at which individuals typically retire from the workforce. These statistics provide valuable insights into trends, patterns, and demographics surrounding retirement age.
Retirement age statistics are important for several reasons. Firstly, they help policymakers and government agencies make informed decisions regarding retirement benefits, social security programs, and workforce planning. By understanding when people are retiring, authorities can better allocate resources and support to ensure the well-being of retirees.
In addition, retirement age statistics are crucial for employers and industries to plan for workforce turnover and succession. By analyzing these statistics, companies can anticipate future labor shortages, skill gaps, and demographic shifts that may impact their operations.
Retirement age statistics are collected through various methods, including surveys, census data, and labor market reports. Researchers and analysts use this data to identify trends, patterns, and factors influencing retirement decisions. By analyzing this information, experts can gain a better understanding of societal changes, economic conditions, and policy impacts on retirement age.
Methods of Collecting Retirement Age Statistics
- Surveys: Researchers conduct surveys to gather information directly from individuals about their retirement plans and decisions.
- Census Data: Government agencies collect data on retirement age as part of national censuses to track population demographics.
- Labor Market Reports: Analysts use labor market reports to analyze trends in retirement age within specific industries and sectors.
Global Retirement Age Trends
Retirement age trends vary significantly across different regions of the world, influenced by a multitude of factors including economic conditions, government policies, and cultural norms.
Comparison of Retirement Age Trends
- In Europe, the retirement age tends to be higher compared to other regions, with countries like France and Italy gradually increasing the retirement age to address aging populations and sustainability of pension systems.
- In North America, the retirement age varies between the United States and Canada, with the former having a higher average retirement age due to a stronger emphasis on individual retirement savings.
- In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea are facing challenges with an aging population, leading to discussions on raising the retirement age to cope with the shrinking workforce.
- In Latin America, retirement age tends to be lower in some countries, reflecting cultural values of early retirement and government policies aimed at creating job opportunities for younger generations.
Factors Influencing Retirement Age Variations
- Economic Stability: Countries with stronger economies often have a higher retirement age as individuals can afford to work longer.
- Government Policies: Social security systems and pension schemes play a significant role in determining the retirement age set by governments.
- Healthcare Access: Access to quality healthcare can impact retirement age, as individuals in better health may choose to work longer.
Impact of Cultural Differences on Retirement Age Statistics
- Cultural Values: Cultural norms around work ethic, family obligations, and leisure time can influence the retirement age in different countries.
- Retirement Expectations: Some cultures may have expectations of early retirement or continued work in later years, shaping retirement age statistics accordingly.
- Gender Roles: Cultural expectations around gender roles and responsibilities can also impact retirement age, with some cultures having different retirement ages for men and women.
Retirement Age by Gender
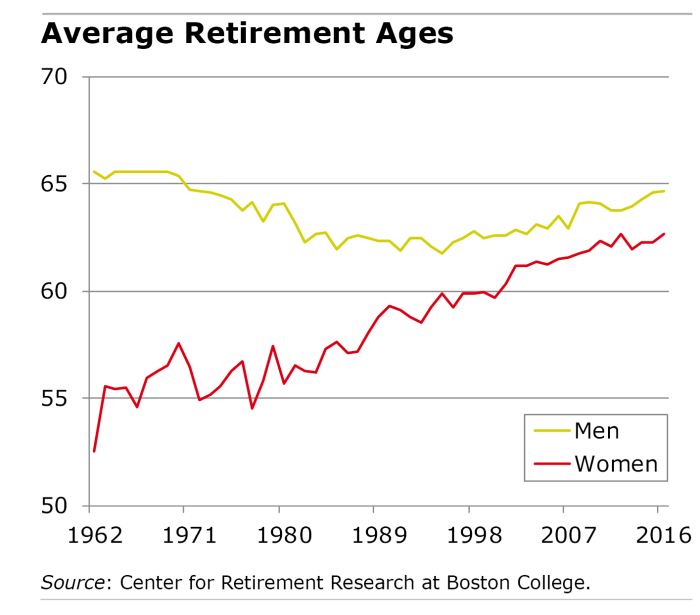
In analyzing retirement age statistics based on gender, it is important to consider the disparities that exist between men and women. These differences can be influenced by a variety of factors, including societal norms and expectations.
Gender Disparities in Retirement Age
- On average, women tend to retire at a younger age than men. This can be attributed to various reasons, such as career interruptions due to caregiving responsibilities or lower average earnings throughout their working years.
- Some studies have also shown that women may face challenges in saving for retirement, leading them to retire earlier than men who may have accumulated more savings.
- Societal expectations around gender roles can also play a significant role in determining retirement age. Traditional norms may pressure women to prioritize family roles over their careers, impacting their financial stability in retirement.
Impact of Societal Norms on Retirement Age
- Gender norms that dictate women should take on more caregiving responsibilities can result in fewer years in the workforce, affecting their ability to save for retirement.
- Conversely, societal expectations for men to be the primary breadwinners may lead them to work longer hours or delay retirement to ensure financial security for their families.
- These societal norms can create a cycle where women retire earlier due to caregiving duties, while men work longer hours to meet financial expectations, perpetuating gender disparities in retirement age.
Retirement Age and Economic Factors
When examining retirement age statistics, it is crucial to consider the impact of economic factors on individuals’ decisions regarding when to retire. Economic conditions play a significant role in determining retirement age, as financial stability and market trends influence the ability of individuals to retire comfortably.
Impact of Economic Factors on Retirement Age
- Economic downturns often lead to individuals delaying their retirement due to financial insecurity. During times of recession, individuals may feel compelled to work longer to build up their savings or recover from financial losses.
- Conversely, during periods of economic prosperity, individuals may choose to retire earlier if they have accumulated enough wealth to support their retirement lifestyle. A strong economy can provide individuals with the confidence to leave the workforce earlier.
- Unemployment rates and job availability also play a role in retirement age decisions. High unemployment rates may force individuals to delay retirement in order to secure a stable income, while a strong job market can provide individuals with more flexibility in choosing when to retire.
Implications of Economic Instability on Retirement Age Statistics
- During times of economic instability, such as market crashes or recessions, retirement age statistics may show a trend of individuals working longer than originally planned. This can have long-term effects on the labor force participation rate and pension system sustainability.
- Economic instability can also impact retirement savings and investment portfolios, leading individuals to reassess their retirement plans and potentially delay retirement to ensure financial security in the future.
- Policies and government interventions in response to economic crises can also influence retirement age decisions. Changes in social security benefits, pension regulations, or tax incentives can impact the timing of retirement for many individuals.
