With Student loan consolidation at the forefront, this paragraph opens a window to an amazing start and intrigue, inviting readers to embark on a storytelling formal with serious tone style filled with unexpected twists and insights.
Student loan consolidation is a crucial financial strategy for many borrowers looking to streamline their debt repayment process. In this guide, we will delve into the concept, types, pros and cons, consolidation process, and the impact on financial health.
What is Student Loan Consolidation?
Student loan consolidation is the process of combining multiple student loans into a single, new loan with a new repayment term and interest rate. This allows borrowers to simplify their loan repayment process and potentially lower their monthly payments.
How Student Loan Consolidation Works
Student loan consolidation works by taking out a new loan to pay off existing student loans. The new loan typically has a fixed interest rate based on the weighted average of the interest rates of the loans being consolidated. Borrowers can choose a new repayment term, which can extend the length of the loan and reduce monthly payments.
- Streamlines repayment: By consolidating multiple loans into one, borrowers only have to make one monthly payment.
- Potentially lower interest rate: The new consolidated loan may have a lower interest rate, saving the borrower money over time.
- Extended repayment term: Consolidation can extend the repayment term, resulting in lower monthly payments but potentially paying more interest over the life of the loan.
- Access to loan forgiveness programs: Consolidated loans may be eligible for certain loan forgiveness programs that were not available with individual loans.
Types of Student Loan Consolidation
When it comes to consolidating student loans, there are different options available to borrowers. It is essential to understand the types of student loan consolidation to make an informed decision based on your financial situation and goals.
Federal Loan Consolidation
Federal loan consolidation allows borrowers to combine multiple federal student loans into one new loan. Here are some key points to consider:
- Federal loan consolidation is only available for federal student loans, not private loans.
- The interest rate for the new consolidated loan is a weighted average of the interest rates on the loans being consolidated, rounded up to the nearest one-eighth of a percent.
- Borrowers can choose a new repayment plan with potentially lower monthly payments and extended loan terms.
Private Loan Consolidation
Private loan consolidation involves refinancing multiple student loans, whether federal or private, into a single private loan with a new lender. Here are some important considerations:
- Private loan consolidation is offered by private lenders, such as banks, credit unions, and online lenders.
- Borrowers may be able to secure a lower interest rate, potentially saving money over the life of the loan.
- Eligibility for private loan consolidation is based on creditworthiness, and borrowers with a good credit score may qualify for better terms.
Eligibility Criteria
- For federal loan consolidation, borrowers must have at least one Direct Loan or Federal Family Education Loan (FFEL) that is in a grace period or repayment.
- Private loan consolidation eligibility depends on the lender’s requirements, typically including a good credit score and stable income.
- Borrowers should carefully review the terms and conditions of both federal and private loan consolidation options before making a decision.
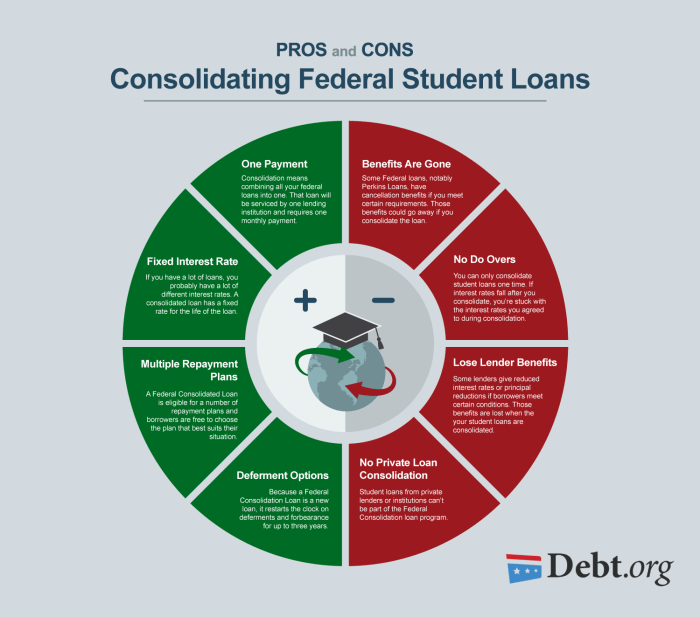
Pros and Cons of Student Loan Consolidation
When considering student loan consolidation, it is crucial to weigh the advantages and disadvantages to make an informed decision. Here are some key points to consider:
Advantages of Student Loan Consolidation
- Lower Monthly Payments: By consolidating multiple loans into one, borrowers can potentially reduce their monthly payments, making it easier to manage their finances.
- Fixed Interest Rate: Consolidation can provide the benefit of a fixed interest rate, protecting borrowers from fluctuations in the market and helping to budget more effectively.
- Simplified Repayment: Dealing with a single loan servicer and payment each month can streamline the repayment process, reducing the risk of missing payments.
- Potential for Loan Forgiveness: Some consolidation programs offer the possibility of loan forgiveness after a certain number of on-time payments, providing relief for borrowers in the long term.
Disadvantages of Student Loan Consolidation
- Extended Repayment Period: While lower monthly payments can be beneficial, extending the repayment period through consolidation may result in paying more interest over time.
- Loss of Benefits: Borrowers may lose certain benefits, such as interest rate discounts or loan forgiveness options, that were available on their original loans.
- Eligibility Criteria: Not all loans are eligible for consolidation, and borrowers may need to meet specific requirements to qualify, limiting their options.
- Potential for Higher Total Cost: Depending on the interest rates of the original loans and the terms of consolidation, some borrowers may end up paying more in the long run.
Real-Life Examples
One example of how consolidation has helped borrowers is Sarah, who was able to simplify her repayment process by combining multiple loans into one. This allowed her to stay on top of her payments and avoid default.
On the other hand, John consolidated his loans but ended up paying more in interest over time due to the extended repayment period. He realized later that he could have saved money by continuing to pay off his loans separately.
It is essential for borrowers to carefully consider their individual circumstances and weigh the pros and cons before deciding whether student loan consolidation is the right choice for them.
How to Consolidate Student Loans
When it comes to consolidating student loans, there are several steps to consider in order to streamline the process and make the best decision based on individual circumstances.
Gather Necessary Documents and Information
- Loan Details: Collect information on all existing student loans, including the lender, balance, interest rate, and repayment terms.
- Financial Information: Prepare proof of income, expenses, and any other relevant financial documents to assess eligibility for different consolidation options.
- Credit Score: Obtain a copy of your credit report to understand your creditworthiness, as it can impact the consolidation terms offered.
Explore Consolidation Options
- Federal Direct Consolidation Loan: Allows you to combine federal student loans into a single loan with a fixed interest rate, based on the average of the loans being consolidated.
- Private Student Loan Consolidation: Involves refinancing multiple private student loans into one new loan with a private lender, potentially offering lower interest rates and better terms.
- Consider Repayment Plans: Evaluate different repayment plans available for consolidation, such as income-driven plans or extended repayment terms, to find the most suitable option for your financial situation.
Choose the Best Consolidation Option
- Compare Interest Rates: Look for consolidation options with the lowest interest rates to minimize the total repayment amount over time.
- Review Terms and Conditions: Pay attention to the terms of the consolidation loan, including repayment terms, fees, and any borrower benefits offered by the lender.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consult with a financial advisor or student loan counselor to get personalized guidance on selecting the best consolidation option based on your unique circumstances.
Impact of Student Loan Consolidation on Financial Health
Student loan consolidation can have a significant impact on an individual’s financial health in various ways. It is essential to understand how consolidation can affect credit scores, repayment terms, and overall financial well-being to make informed decisions. Additionally, managing finances post-consolidation is crucial to avoid future debt issues.
Credit Score Implications
Consolidating student loans can have both positive and negative effects on credit scores. On one hand, consolidating multiple loans into a single payment can simplify repayment and make it easier to stay on track. However, applying for a new loan or credit account can result in a temporary decrease in credit score due to the hard inquiry. It is important to weigh the benefits of consolidation against the potential impact on credit scores before making a decision.
Repayment Terms and Financial Well-being
Consolidating student loans can also impact repayment terms and overall financial well-being. By combining multiple loans into one, borrowers may be able to secure a lower interest rate, extend the repayment period, or change the type of repayment plan. This can result in lower monthly payments and make it easier to manage debt. However, extending the repayment period may lead to paying more in interest over time. It is essential to carefully consider the trade-offs and implications of consolidation on long-term financial goals.
Strategies for Managing Finances Post-Consolidation
After consolidating student loans, it is crucial to develop a solid financial plan to avoid future debt issues. This includes creating a budget, tracking expenses, building an emergency fund, and exploring additional ways to save money. Setting financial goals, such as paying off debt or saving for major expenses, can help individuals stay motivated and on track. Regularly reviewing and adjusting the financial plan as needed is key to maintaining financial health post-consolidation.
