Diving into the intricacies of mutual funds, this introduction sets the stage for a detailed exploration of this investment vehicle. From unraveling the complexities to shedding light on the benefits, this guide aims to provide a solid foundation for understanding mutual funds.
Exploring different types, how they function, and the risks involved, readers will gain valuable insights into the world of mutual funds.
What are mutual funds?
Mutual funds are investment vehicles that pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. These funds are managed by professional portfolio managers who make decisions on behalf of the investors.
Types of mutual funds
- Equity Funds: These funds primarily invest in stocks, offering potential for high returns but also higher risk.
- Bond Funds: These funds invest in government or corporate bonds and are generally lower risk compared to equity funds.
- Money Market Funds: These funds invest in short-term, low-risk securities and are often used as a cash alternative.
- Index Funds: These funds track a specific market index, such as the S&P 500, and aim to replicate its performance.
Benefits of investing in mutual funds
- Mutual funds provide diversification, allowing investors to spread their risk across various assets.
- Professional management by experienced fund managers can help investors navigate the complexities of the market.
- Liquidity, as investors can easily buy or sell mutual fund shares at their net asset value (NAV) at the end of each trading day.
- Accessibility, as mutual funds allow investors to start investing with relatively small amounts of money.
How do mutual funds work?
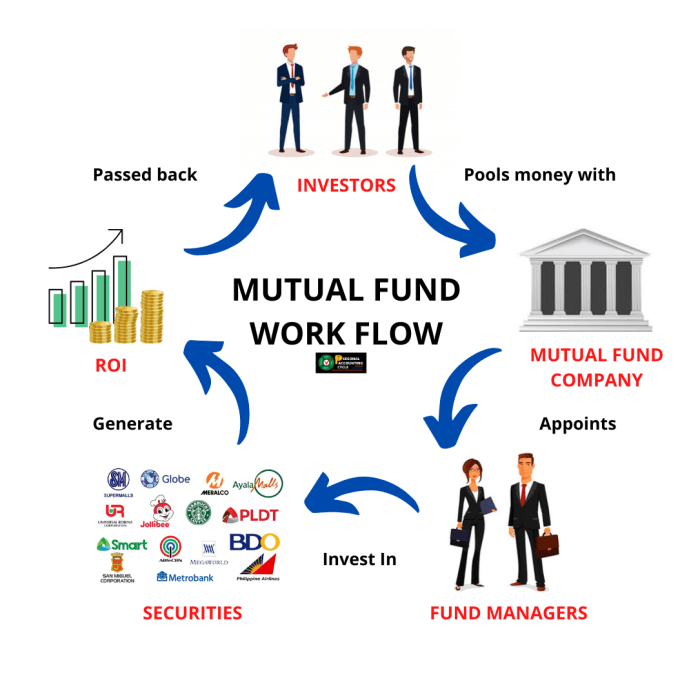
When it comes to understanding how mutual funds operate, it is essential to grasp the basic concept of pooling money from various investors to create a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. This pooling of resources allows individual investors to access a wide range of investment opportunities that may not be feasible on their own.
Role of a fund manager in managing mutual funds
Fund managers play a crucial role in managing mutual funds by making investment decisions on behalf of the fund’s investors. They are responsible for researching, selecting, and monitoring the securities held within the fund’s portfolio. Fund managers aim to achieve the fund’s investment objectives and maximize returns for investors while managing risk.
- Fund managers conduct in-depth research and analysis to identify investment opportunities that align with the fund’s objectives and risk tolerance.
- They regularly monitor the performance of the fund’s holdings and make adjustments to the portfolio as needed to optimize returns and manage risk.
- Fund managers also communicate with investors through regular reports and updates on the fund’s performance and investment strategy.
Process of buying and selling mutual fund shares
Investors can buy and sell mutual fund shares through the fund’s issuing company or a brokerage firm. The process involves the following steps:
- Investors place an order to buy or sell mutual fund shares through the fund company or brokerage firm.
- The price at which the shares are bought or sold is based on the fund’s net asset value (NAV), which is calculated at the end of each trading day.
- When buying mutual fund shares, investors may incur sales charges or fees, depending on the type of fund and the sales structure.
- When selling mutual fund shares, investors may be subject to redemption fees or charges, especially for short-term holdings.
Types of mutual funds
Mutual funds can be categorized into different types based on the assets they invest in and their management style. Understanding these categories can help investors make informed decisions about their investments.
Equity funds
Equity funds primarily invest in stocks or shares of companies. These funds aim to provide growth and capital appreciation over the long term. They can be further classified based on market capitalization, such as large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap funds.
Bond funds
Bond funds invest in fixed-income securities like government or corporate bonds. These funds are considered less risky compared to equity funds and are suitable for investors looking for regular income and capital preservation.
Index funds
Index funds mirror a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. These funds aim to replicate the performance of the index they track, offering diversification and lower expenses compared to actively managed funds.
Actively managed funds vs. Passively managed funds
Actively managed funds have a fund manager who makes investment decisions to outperform the market. These funds involve higher fees and are more actively traded. On the other hand, passively managed funds aim to replicate the performance of a specific index and have lower fees due to minimal trading.
Risk associated with different types of mutual funds
Equity funds are considered riskier than bond funds due to the volatility of the stock market. However, they also offer higher return potential. Bond funds are relatively less risky but may not provide the same level of returns as equity funds. Index funds carry market risk but offer diversification benefits and lower expenses compared to actively managed funds.
Advantages and disadvantages of mutual funds
Investing in mutual funds offers several advantages, such as diversification, professional management, liquidity, and convenience. However, there are also potential drawbacks and risks associated with mutual funds that investors should consider. Here, we will explore the advantages, disadvantages, and provide tips on how to mitigate risks when investing in mutual funds.
Advantages of mutual funds
- Mutual funds provide diversification by investing in a variety of securities, reducing the risk of significant loss from a single investment.
- Professional management: Mutual funds are managed by experienced fund managers who make investment decisions on behalf of investors based on research and market analysis.
- Liquidity: Investors can easily buy or sell mutual fund shares at the end of each trading day, providing liquidity compared to other investment options like real estate or fixed deposits.
- Convenience: Mutual funds offer a convenient way for investors to access a diversified portfolio without the need to research individual stocks or bonds.
Disadvantages and risks of mutual funds
- Fees and expenses: Mutual funds charge management fees and expenses, which can reduce overall returns for investors.
- Market risk: Mutual funds are subject to market fluctuations, and the value of the fund can go up or down based on the performance of the underlying securities.
- Lack of control: Investors have limited control over the specific securities in the mutual fund portfolio, as investment decisions are made by the fund manager.
- Tax implications: Capital gains from mutual funds are taxable, and investors may face tax consequences when redeeming their fund shares.
Tips to mitigate risks when investing in mutual funds
- Do thorough research before investing in a mutual fund to understand the fund’s objectives, past performance, and fees.
- Diversify your investments across different asset classes and mutual funds to reduce risk.
- Regularly review your investment portfolio and consider rebalancing to align with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
- Consider consulting with a financial advisor to get personalized advice on selecting mutual funds that align with your investment objectives.
How to choose a mutual fund
Choosing the right mutual fund is crucial for achieving your financial goals and managing risk effectively. There are several factors to consider when selecting a mutual fund, including your risk tolerance, investment goals, time horizon, and financial situation.
Factors to consider when selecting a mutual fund
- Assess your risk tolerance: Determine how much risk you are willing to take on based on your comfort level and financial goals.
- Define your investment goals: Clearly Artikel your objectives, whether you are looking for growth, income, or a combination of both.
- Evaluate your time horizon: Consider how long you plan to invest in the mutual fund before needing to access the funds.
- Analyze your financial situation: Take into account your current financial position, income level, and existing investments.
Methods of evaluating mutual funds
- Performance: Look at the historical performance of the mutual fund to assess its track record and consistency.
- Expenses: Consider the fees and expenses associated with the mutual fund, including management fees and operating costs.
- Historical data: Review the fund’s past performance over different market cycles to understand how it has performed in various market conditions.
Step-by-step guide on how to research and choose the right mutual fund
- Define your investment goals and risk tolerance.
- Research different types of mutual funds that align with your objectives.
- Compare the performance and expenses of the funds you are considering.
- Read the fund’s prospectus to understand its investment strategy and objectives.
- Consider seeking professional advice from a financial advisor for personalized recommendations.
