Delving into the world of stock options, this guide aims to provide a detailed insight into the intricacies of this financial instrument.
Exploring the nuances of stock options, from their definition to the various strategies employed, this guide is designed to equip readers with a thorough understanding of this complex topic.
What are Stock Options?
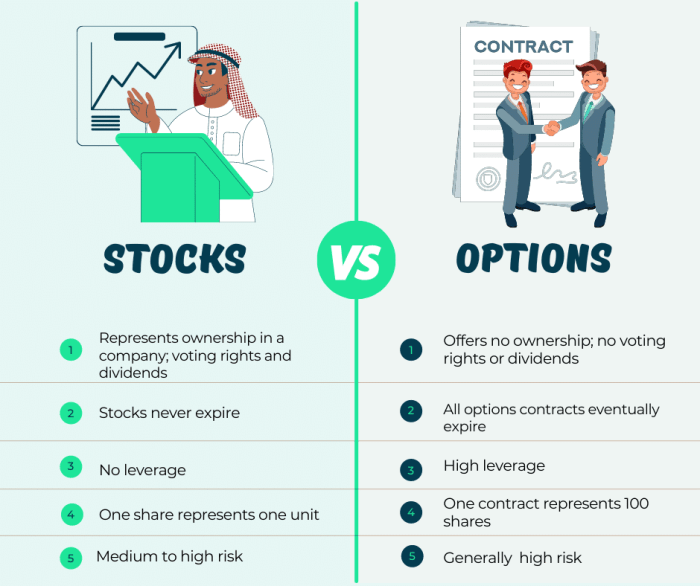
Stock options are financial instruments that give individuals the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific stock at a predetermined price within a set timeframe. Unlike stocks, which represent ownership in a company, stock options provide the opportunity to profit from the movement of stock prices without actually owning the underlying stock.
Types of Stock Options
- Call Options: Call options give the holder the right to buy a specific stock at a predetermined price, known as the strike price, before the expiration date.
- Put Options: Put options give the holder the right to sell a specific stock at a predetermined price, known as the strike price, before the expiration date.
How Stock Options Work
When an investor purchases a stock option, they pay a premium to the option seller. The premium is the cost of buying the option and is determined by factors such as the stock price, strike price, and time until expiration. If the option is not exercised before the expiration date, it expires worthless.
Benefits of Stock Options
Stock options offer several advantages for investors, making them a valuable tool in the financial market. Let’s explore the benefits of using stock options, compare them to other investment tools, and understand how they can be utilized for risk management and hedging strategies.
Advantages of Stock Options
- Leverage: Stock options allow investors to control a larger number of shares with less capital, amplifying potential returns.
- Flexibility: Options provide the flexibility to tailor investment strategies based on market conditions and individual risk tolerance.
- Diversification: Investors can use stock options to diversify their portfolio without the need to directly purchase large quantities of individual stocks.
Comparison with Stocks and Bonds
- Risk Management: Unlike stocks, options limit the potential loss to the premium paid, offering a defined risk profile. Bonds, on the other hand, provide fixed income but lack the potential for capital appreciation that stock options offer.
- Profit Potential: Stock options offer the potential for significant returns through leverage, which is not typically available with stocks or bonds.
- Cost Efficiency: Options require less capital upfront compared to purchasing stocks outright, making them a cost-effective way to gain exposure to the market.
Utilizing Stock Options for Risk Management
- Hedging Strategies: Investors can use options to hedge against potential losses in their stock holdings, providing downside protection in volatile markets.
- Income Generation: Selling covered calls can generate income for investors while offsetting potential downside risk in their stock positions.
- Portfolio Protection: By incorporating put options in their portfolio, investors can safeguard against market downturns and preserve capital.
Risks Associated with Stock Options
When trading stock options, investors are exposed to various risks that can result in financial loss. It is essential to understand these risks before engaging in options trading to make informed decisions.
Leverage in Stock Options
One of the key risks associated with stock options is the concept of leverage. Options contracts allow investors to control a large number of shares with a relatively small amount of capital. While leverage can amplify gains, it can also magnify losses. For example, if an investor purchases a call option for a stock at a strike price of $50 with a premium of $2 per share, they have the right to buy 100 shares at $50 each. If the stock price drops below $50, the investor could potentially lose the entire premium paid for the option.
Volatility and Time Decay
Another risk factor in stock options trading is volatility and time decay. Options prices are influenced by the volatility of the underlying stock and the passage of time. High volatility can lead to significant price swings in options, increasing the risk of loss. Additionally, as options approach their expiration date, they lose value due to time decay. This means that even if the underlying stock price moves in the desired direction, the option may still lose value over time.
Market and Liquidity Risks
Market risks also play a significant role in options trading. Factors such as economic events, geopolitical issues, and overall market conditions can impact the price of options. Furthermore, liquidity risk is a concern, as low trading volumes in certain options contracts can lead to wider bid-ask spreads and difficulty in executing trades at desired prices.
Assignment and Margin Risks
When trading options, there is a risk of assignment, where the seller of an option may be required to fulfill their obligation to buy or sell the underlying stock. This can result in unexpected costs or losses for the seller. Additionally, margin requirements for options trading can expose investors to margin calls if the value of the option position deteriorates, leading to the need for additional funds or the forced liquidation of the position.
Factors Influencing Stock Options
Factors influencing stock options play a crucial role in determining their pricing and value. Understanding these factors is essential for investors and traders to make informed decisions in the options market.
Market Conditions
Market conditions have a significant impact on stock options pricing. The overall market sentiment, economic indicators, geopolitical events, and other external factors can influence the demand and supply of options, leading to fluctuations in prices.
Volatility
Volatility is a key factor affecting stock options. Higher volatility increases the likelihood of price swings, making options more valuable. On the other hand, low volatility reduces the potential for price movements, resulting in lower option prices.
Time to Expiration
The time remaining until the expiration of an option contract also plays a crucial role in its pricing. As the expiration date approaches, the time value of the option decreases, impacting its overall value. Shorter expiration periods typically result in lower option prices.
Interest Rates
Interest rates can affect stock options pricing through their impact on the cost of carry. Changes in interest rates can influence the cost of holding an option position, thereby affecting its value. Higher interest rates generally lead to higher option prices.
Dividends
Dividends paid by the underlying stock can impact the pricing of stock options. When a stock pays a dividend, the price of the stock typically decreases by the dividend amount. This decrease can influence the value of options on the stock.
Strategies for Trading Stock Options
When it comes to trading stock options, various strategies can be utilized to achieve different objectives. Understanding these strategies is crucial for successful trading in the options market.
Common Strategies Used in Trading Stock Options
- Covered Calls: This strategy involves selling call options on a stock that is already owned. It allows investors to generate income from the premiums collected.
- Protective Puts: This strategy involves buying put options to protect against a potential decline in the stock price. It acts as insurance for the stock position.
- Long Straddle: This strategy involves buying both a call option and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date. It profits from significant price movements in either direction.
- Iron Condor: This strategy involves combining a bear call spread and a bull put spread to profit from a stock that trades within a specified range.
Comparison of Long and Short Options Strategies
- Long Options Strategies: Long strategies involve buying options with the expectation of price movements in the underlying stock. They offer unlimited profit potential but come with limited risk (the premium paid).
- Short Options Strategies: Short strategies involve selling options with the expectation of the options expiring worthless. They offer limited profit potential (the premium received) but come with potentially unlimited risk.
Importance of Understanding Technical Analysis
Technical analysis plays a crucial role in trading stock options as it helps traders identify patterns, trends, and key levels that can influence their trading decisions. By analyzing historical price data and chart patterns, traders can make more informed choices when entering and exiting option positions.
